• Geopolitical tensions emerged as biggest challenge in 2023
• Surveyed companies showed increased interest in digital currencies
• Financial institutions remain more conservative in digital adoption
Over the past decade, China has expanded its financial market exposure, gradually fostering the internationalisation of the Renminbi (RMB).
Despite geopolitical shifts and widening interest rate differentials, China’s positive macroeconomic outlook and technological innovation present favourable conditions for the RMB in global trade and investment.
In 2023, China Construction Bank and The Asian Banker conducted a comprehensive survey on the international use of the RMB for cross-border trade settlement, cash management, investment, and financing. The study encompassed 2,542 executives from Chinese companies, overseas companies, and global financial institutions (FI).
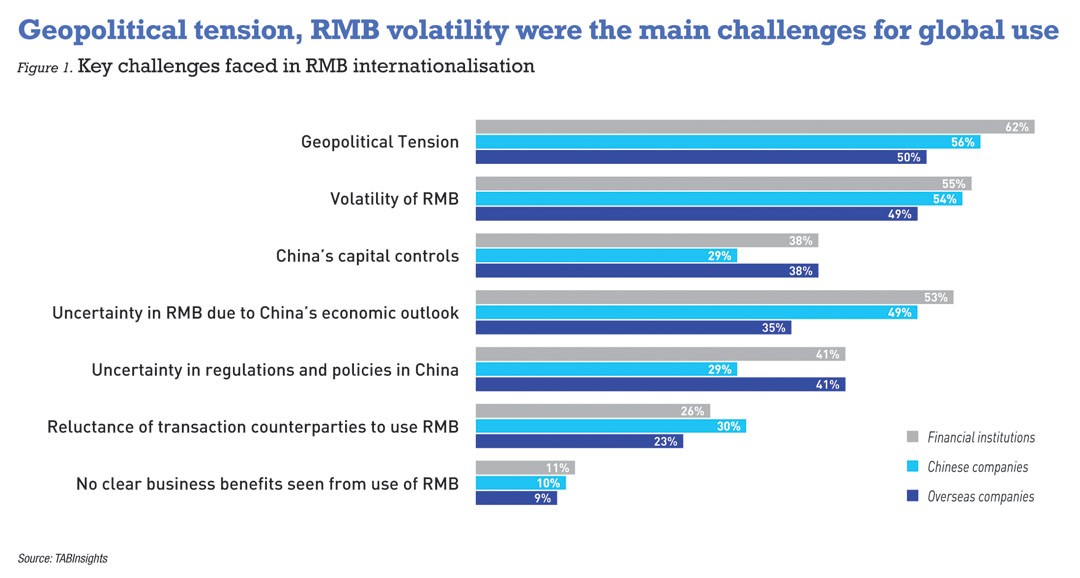
Geopolitical tensions emerged as biggest challenge in 2023
The survey showed that geopolitical tensions are the primary concern for respondents across various groups. Overseas companies cite it as their top challenge, with 50% of respondents, up from 45% in 2022. For Chinese companies, this dropped from 74% in 2022 to 56%. The figure remained constant at 62% for FI.
About 55% of FI, 54% of Chinese companies, and 49% of overseas companies cited the volatility of the RMB as the second biggest challenge, up from 53%, 48% and 34%, respectively, in 2022. It is worth mentioning that Chinese and overseas companies had diverging views on the impact of China’s economic outlook.
Survey results showed that 49% of Chinese companies regarded uncertainty in China’s economic outlook as a major challenge, a sharp rise from 37% in 2022; for overseas companies, this decreased from 53% to 35% in 2023. The view for FI remained relatively constant in this regard at 53%, just one percentage point lower than in 2022.
 Nevertheless, the RMB internationalisation process remains on track due to factors such as China’s implementation of bilateral and regional free-trade agreements, the increasing adoption of local currencies in cross-border transactions by individual countries, and progress in digitalising the cross-border trading ecosystem.
Nevertheless, the RMB internationalisation process remains on track due to factors such as China’s implementation of bilateral and regional free-trade agreements, the increasing adoption of local currencies in cross-border transactions by individual countries, and progress in digitalising the cross-border trading ecosystem.
When asked about the interest in using digital e-commerce for cross-border operations, all three categories of institutions expressed support, with 75% of overseas companies, 59% of FI, and 57% of Chinese companies stating they are aware and have used e-commerce platforms to some extent.
Surveyed institutions were also asked about their prospects for using digital currencies in financial transactions. Both overseas and Chinese companies showed increased interest compared to two years ago, given that more use cases abound in both retail and commercial sectors around the globe. The survey indicated that 80% of overseas companies and 56% of Chinese companies are willing to use digital currencies for financial transactions, compared to 62% and 30%, respectively, in 2022. The number of respondents undecided or unwilling to use digital currencies dropped significantly for both groups, from 35% and 68%, respectively, in 2022 to just 19% and 43% in 2023.
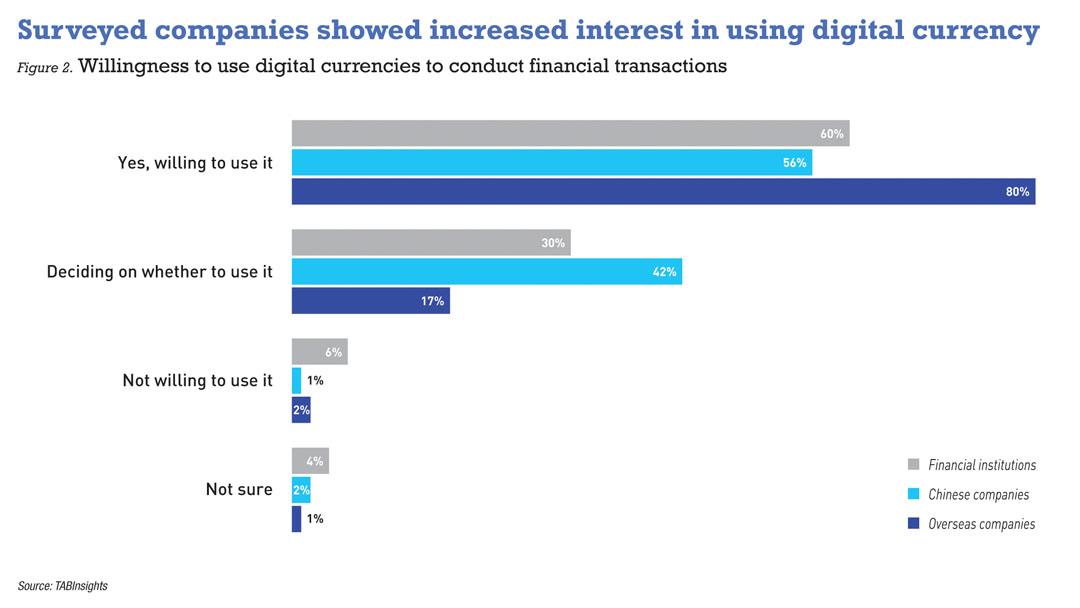 FI remain more conservative in digital adoption than surveyed companies
FI remain more conservative in digital adoption than surveyed companies
Conversely, FI are more conservative than surveyed companies in adopting digital currencies in their transactions. Interest among FI decreased by two percentage points from two years ago to 60% in 2023, while those undecided or unwilling to use digital currencies increased from 34% to 36%.
The full report is available in both English and Chinese, spanning a total of 110 pages. Download it here: https://reports.tabinsights.com/reports/rmb-internationalisation-report





































